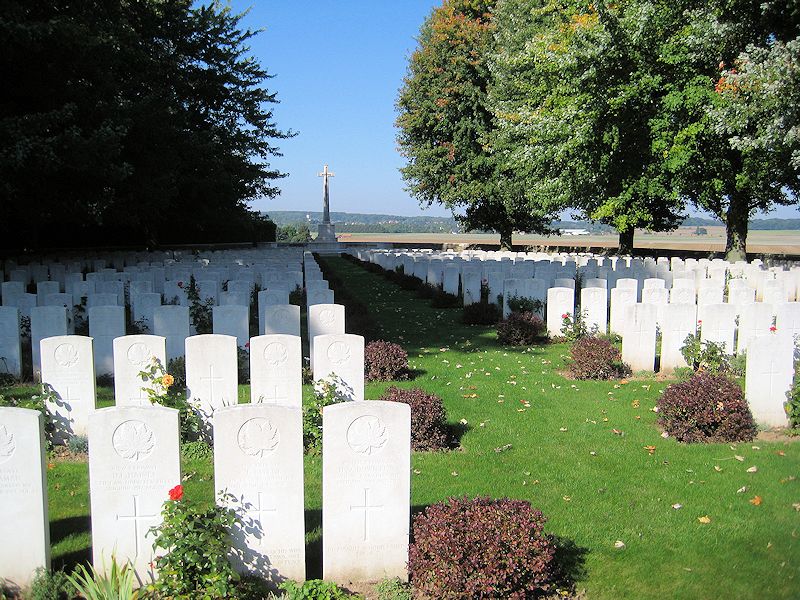
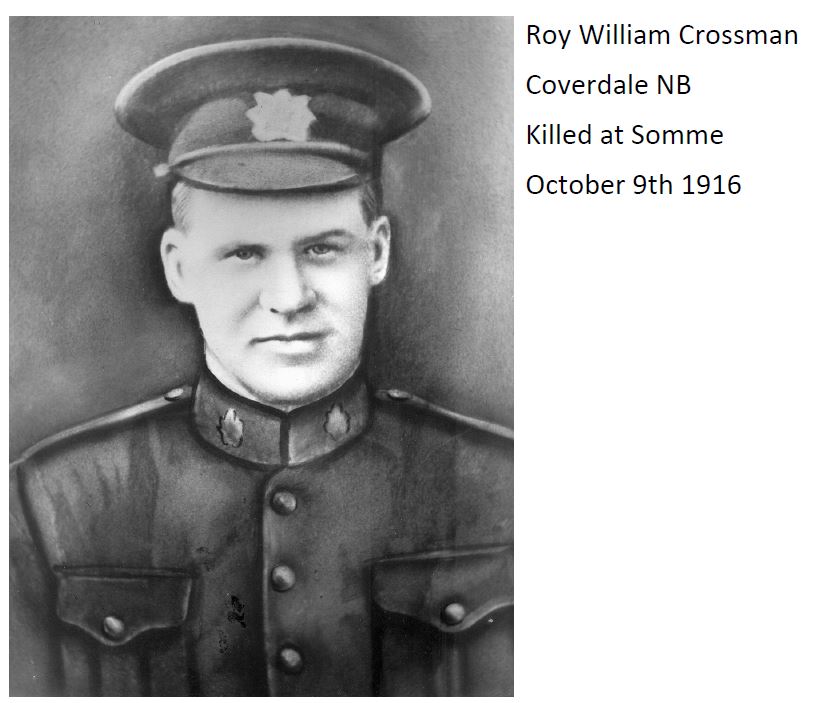
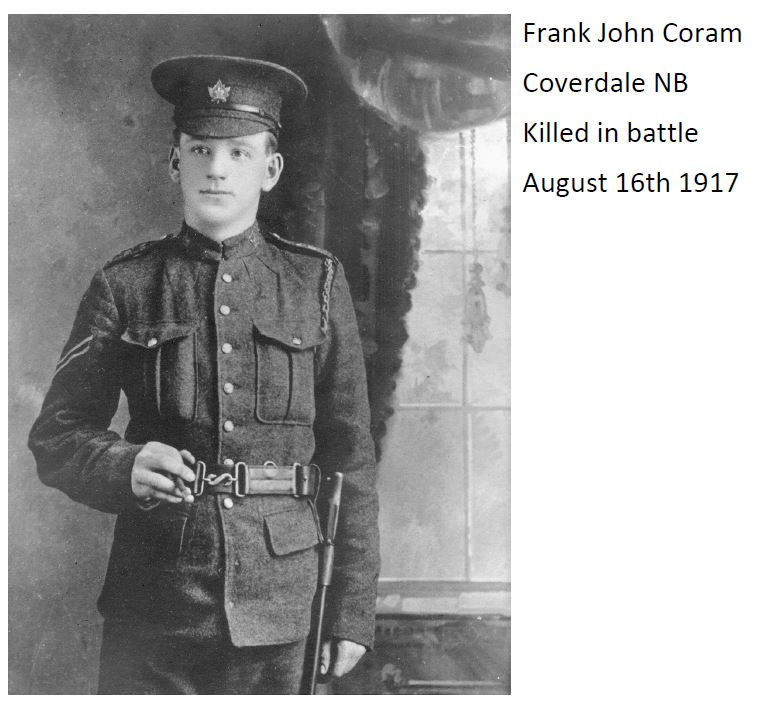
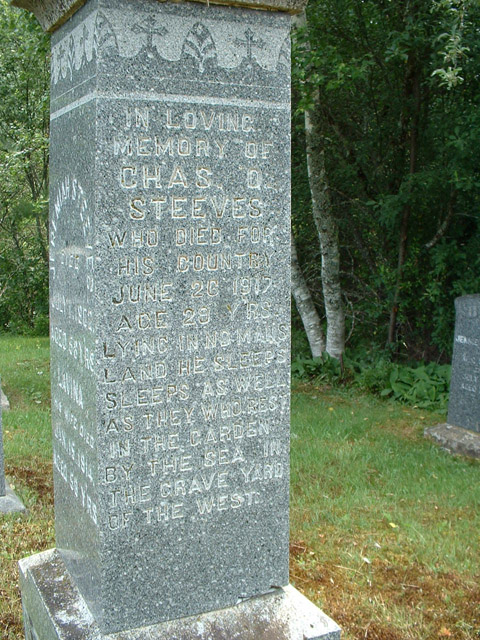On November 8, 2019 the Albert County Museum and RB Bennett Commemorative Centre with The Royal Canadian Legion Branch 32 (Hillsborough) will be planting 75 Liberation75 Tulips in celebration of the liberation of the Netherlands in 1945 by the 1st Canadian Army and to commemorate the 1.1 million Canadians who served in the Second World War.
It happens that November 8 , 2019 is 75 years to the day that ended the Battle of Scheldt.
In early October 1944, the Allies controlled the harbours north of the Seine but the supply issue was not yet solved: Dieppe, Le Tréport and Ostende had been opened but could not handle the high volumes that Allied troops in Europe required. Le Havre, Boulogne and Calais were not serviceable having suffered major destructions. Further north, Antwerp had been liberated by the Allies on September 3rd, but the city was located on the Scheldt River, some 80 kilometres from the open sea and the river’s mouth was still under German control. The only way to make sure that the supplies required by the campaign in Europe could enter the continent was to capture the Scheldt. This was to be the mission of the First Canadian Army.
The marshes south of the Scheldt Estuary was defended by German troops in an area the Allies named the Breskens pocket. The terrain posed the largest threat for the advancing Allied troops, where the flooded fields not only slowed the attackers, but it also provided cover for the defending German troops from both land and aerial reconnaissance. The 3rd Canadian Infantry Division's 7th Brigade moved across the Leopold Canal while the 9th Brigade mounted an amphibious attack on the northern coast on 6 Oct; the two Canadian brigades secured the area near the Aardenburg road by 12 Oct. Meanwhile, the 8th and 9th Brigades asserted pressure from different directions to overwhelmed the Germans in the pocket. This operation was named Operation Switchback, and it ended on 3 Nov after securing Knokke and Zeebrugge, eliminating German threat on the south coast of the Scheldt Estuary.
The island stronghold of Walcheren was attacked from the air, with British Royal Air Force aircraft targetting dykes, flooding the island. The flooding hampered German movement, and also raised the water levels so that the Allies could have deeper water for an amphibious operation. As predicted by Eisenhower, the capture of this island "required a joint naval, air, and ground operation," and it was exemplified with this successful coordination between bombers and ground troops. On 31 Oct Canadian troops attacked across the single causeway between Walcheren and South Beveland, supported by an amphibious assault on 1 Nov from the south across the estuary. On 6 Nov, the island's capital Middelburg fell, and the island was declared secure two days later.
After a month of fighting, the Allied victory came at a high cost of 12,873 casualties among the veterans of Falaise and Caen, half of them Canadian. Meanwhile, the victors captured 41,043 prisoners. With the hostile forces cleared from the area, time-consuming mine-clearing operations could finally begin. Antwerp opened as an Allied port on 28 Nov. "The end of Nazism was in clear view when the first ship moved unmolested up the Scheldt", said Eisenhower. This first vessel to arrive at Antwerp was appropriately the Canadian-built freighter Fort Cataraqui. The gallantry that the Canadian soldiers had shown amidst fierce fighting earned utmost respect of Montgomery. "The Canadians have proved themselves magnificent fighters. Clearing the Scheldt was a job that could have been done only by first-rate troops. Second-rate troops would have failed."
The planting ceremony will take place at the Albert County Museum on Friday, November 8 at 2pm.
The text on the Battle of Scheldt was taken verbatim from https://ww2db.com/battle_spec.php?battle_id=116 .